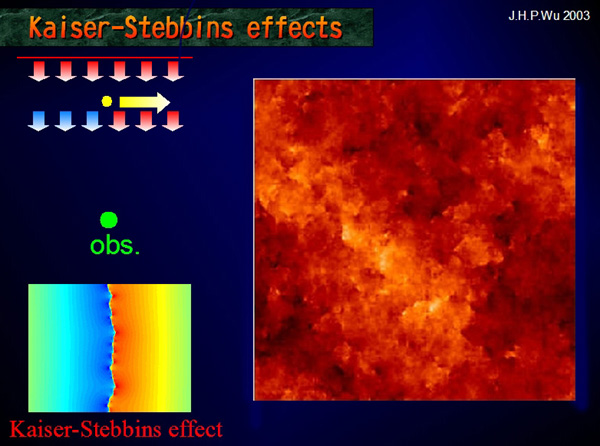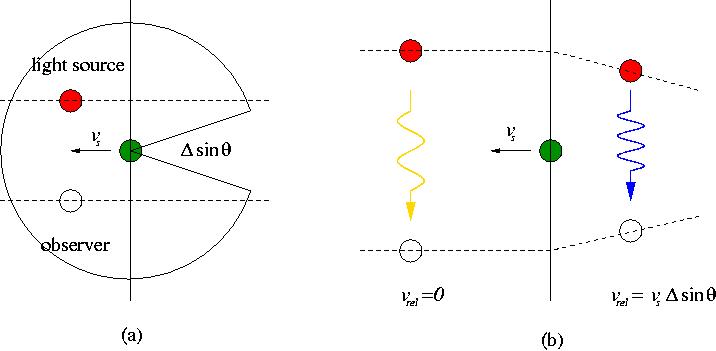
Figure 6. The Kaiser-Stebbins effect is originated from conic space-time around the cosmic string, which is a filamentary form of vacuum energy. A moving cosmic string induces relative speed between the light source and observer and causes a Doppler shift of photons. In the figure,
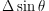 represents
the effective deficit angle viewed from observer.
represents
the effective deficit angle viewed from observer. The height of temperature step caused by a moving cosmic string is given by
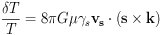
where
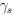 = Lorentz factor for string segment, vs
= string segment velocity, s =
orientation of segment unit vector and k
= line of sight unit vector.
= Lorentz factor for string segment, vs
= string segment velocity, s =
orientation of segment unit vector and k
= line of sight unit vector.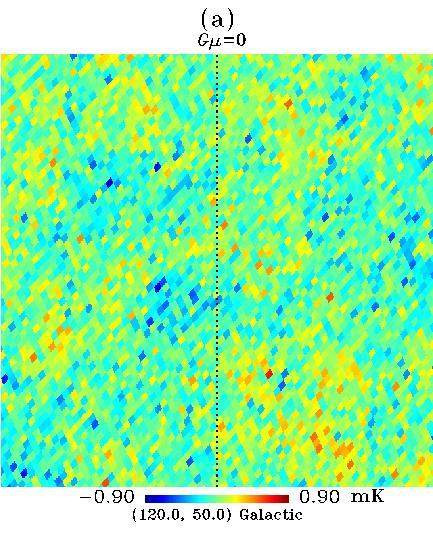
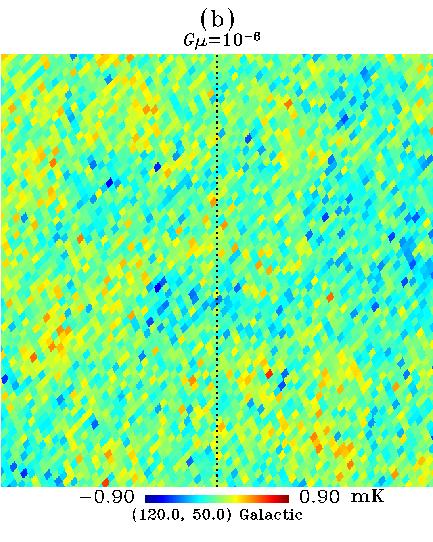
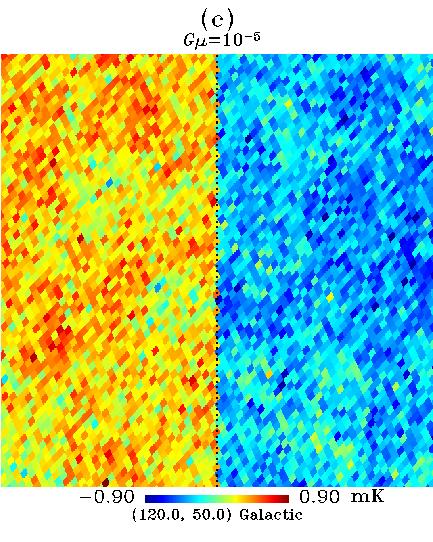
Figure 7. (a) A rectangular patch of real CMB anisotropy map (WMAP 1st-year W-band),
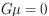 . (b) A straight cosmic string with
. (b) A straight cosmic string with 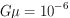 moving to
the right is input. The dotted vertical line indicates the string. It
is hard to recognize the temperature step produced by the cosmic
string. (c) A more powerful string is input,
moving to
the right is input. The dotted vertical line indicates the string. It
is hard to recognize the temperature step produced by the cosmic
string. (c) A more powerful string is input, 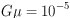 . Now it clearly shows the
temperature contrast caused by the cosmic strings. In this simulation,
we set
. Now it clearly shows the
temperature contrast caused by the cosmic strings. In this simulation,
we set 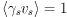 .
.